The first three sub-clauses of Article 17 of Macau’s shiny new gaming law, passed just last week, provide:
17.1. The share capital of concessionaires cannot be less than MOP$5 billion, and their net assets cannot be less than that amount during the concession period.
17.2. Concessionaires are required to prove that the share capital is paid up in cash and must prove that it is deposited in a credit institution authorized to operate in the Macau SAR.
17.3. The deposit referred to in the previous sub-clause cannot be used by the concessionaires before the start of their activities.
This minimum capital requirement for Macau concessionaires was a mere MOP$200 million last time around in 2002. So that’s a 25-fold increase to MOP$5 billion (US$625 million), quite a hike compared to the increase in GGR and GDP in that 20-year period, which are 13x and 7x respectively.
New companies making a concession tender bid (if there are any given the current dreadful economic situation in Macau – a subject best left for another day) will need to establish a Macau S.A. (Sociedade Anónima) company, open a bank account, stick a lazy MOP$5 billion in it and make a bid. If they win a concession, they will be required to wait for the government to give the green light to start operating and from that day onwards they can use the money to establish their business. Sounds easy if you say it quickly.
But what about the current Macau concessionaires? This is where things get a little more complex. The six existing concessionaires – GEG, MRE, MGM, SCL, SJM and Wynn – all have Macau-registered S.A. companies which hold concession contracts with the Macau government, and which have been operating Macau casinos for the best part of two decades. Here’s a snapshot of relevant balance sheet data for them at the end of last year:
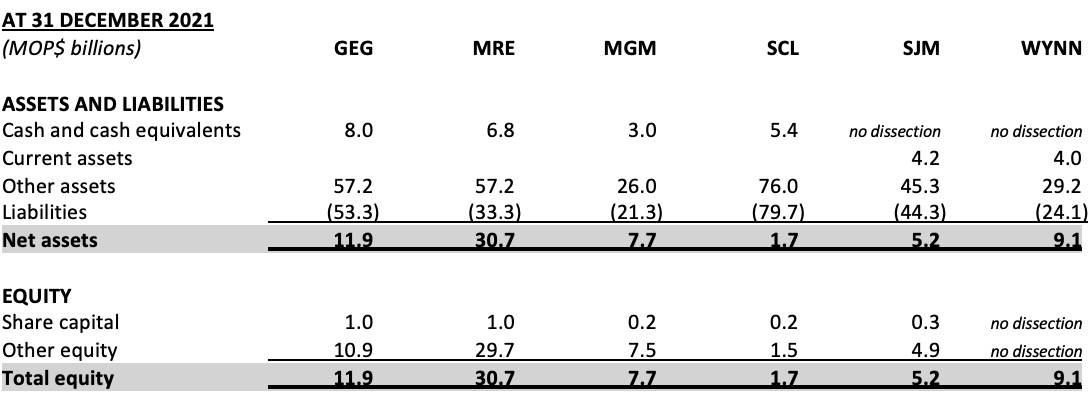 For the avoidance of confusion, it should be noted the above financial data relates only to the Macau-registered license-holder subsidiary, not the listed parent company.
For the avoidance of confusion, it should be noted the above financial data relates only to the Macau-registered license-holder subsidiary, not the listed parent company.
Note the share capital amounts range from the former minimum MOP$200 million for MGM and SCL up to MOP$1 billion for GEG and MRE. Wynn’s total equity is shown as MOP$9.1 billion without dissection but based upon the other five, I suspect its share capital is probably MOP$200 million, or perhaps a little more, but nowhere near the new MOP$5 billion requirement. So at least five, and probably all six, must issue additional share capital of at least MOP$4 billion, and in some cases as much as MOP$4.8 billion. In fact, technically speaking, they should already have done it, since the new Macau gaming law came into force when it was gazetted on Wednesday last week (22 June). Perhaps they have.
Under article 17.2 the MOP$5 billion in share capital is required to be “paid up in cash.” Most likely the government will simply interpret this as each of the existing six concessionaires needing to prove they have MOP$5 billion in cash in the bank at the time they submit their tender bids. Galaxy, Melco and Sands all satisfied this requirement at 31 December 2021, but MGM, SJM and Wynn will likely have to inject cash into their concessionaire entities to get them across the line.
It seems the simplest thing for each of the six of them to do is to bite the bullet, issue MOP$5 billion in additional share capital and pay it all up in cash. Sure, Galaxy and Melco could get away with MOP$4 billion, but do they really want the government to see them scrimping in that way?
So that’s another US$625 million times six in cash for the industry to find, in the middle of this COVID crisis while they’re all bleeding hundreds of millions each quarter. This is yet another impost on an already very battered and bruised industry.
Macau’s concessionaires have long been seen as bottomless pits of money, but companies can’t just keep borrowing and borrowing and borrowing money ad infinitum. If Macau keeps going the way it has been for the past two years, the well is going to dry up sooner or later. And it might be sooner than we all think.


































